What are Omega 3 and 6 Essential Fatty Acids? Well, in the world of nutrition, few topics have garnered as much attention as omega fatty acids. These essential nutrients play a crucial role in our overall health, particularly when it comes to heart and brain function. But with so much information out there, it can be challenging to understand how to properly balance these fats in our diet. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, exploring their benefits, sources, and the importance of maintaining the right balance for optimal health.

Understanding Omega Fatty Acids
Omega fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats that our bodies cannot produce on their own. This means we must obtain them through our diet, making them “essential” nutrients. The two main types we’ll focus on are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
The Historical Perspective
Before delving into the specifics of each type, it’s crucial to understand how our consumption of these fats has changed over time. Before the introduction of seed and vegetable oils (sunflower, rapeseed, soy, chia seed oils, etc.) into our diet in the 1900s, humans actually ate very few processed seed products. Seeds and seed oils are very high in Linoleic Acid, the principal Omega-6 which becomes very inflammatory when we consume too much–particularly if the oil has been oxidized, heated, or chemically processed.
The increase in seed oil consumption has warped our Omega-3 to 6 ratios, and we have transitioned from a healthy 1:1 ratio to a 1:20 ratio in the last few centuries. This dramatic shift has significant implications for our health, as we’ll explore further.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Heart and Brain’s Best Friend
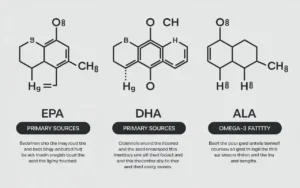
Omega-3s have gained significant attention in recent years due to their numerous health benefits. There are three main types of omega-3s:
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
EPA and DHA are primarily found in fatty fish and seafood, while ALA is found in plant sources like flaxseeds and chia seeds.
Benefits of Omega-3s:
- Heart Health: Omega-3s have been shown to reduce triglycerides, lower blood pressure, and decrease the risk of heart disease and stroke
- Brain Function: DHA, in particular, is crucial for brain development and may help improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases
- Inflammation Reduction: Omega-3s have potent anti-inflammatory properties, which can help manage chronic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease
- Mental Health: Regular consumption of omega-3s has been linked to a lower risk of depression and may help alleviate symptoms in those already diagnosed
- Eye Health: DHA is a major structural component of the retina, and adequate intake may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration
Omega-6 Fatty Acids: The Double-Edged Sword
Omega-6 fatty acids are also essential for our health, but the modern Western diet often contains an excess of these fats. The most common omega-6 fatty acid is linoleic acid, which is found in vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds.
Benefits of Omega-6s:
- Energy Production: Omega-6s play a crucial role in providing energy for the body.
- Brain Function: Like omega-3s, omega-6s are important for brain health and development.
- Skin Health: Adequate omega-6 intake is necessary for maintaining healthy skin and hair.
- Hormone Regulation: Omega-6s are involved in the production of certain hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
The Importance of Balance
While both omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are essential, the key to optimal health lies in maintaining the right balance between the two. In the typical Western diet, the ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 is often as high as 20:1, when ideally, it should be closer to 4:1 or even 1:1
An imbalance favoring omega-6s can lead to increased inflammation in the body, which is associated with various chronic diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. On the other hand, a diet rich in omega-3s can help counteract this inflammation and promote overall health.
How to Achieve the Right Balance
Balancing your omega-3 and omega-6 intake doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some practical tips to help you achieve the right balance:
- Increase Omega-3 Intake:
- Eat fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, or sardines at least twice a week
- Include plant-based sources of ALA like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts in your diet.
- Consider a high-quality fish oil supplement if you don’t consume enough fish.
- Moderate Omega-6 Intake:
- Reduce consumption of processed foods and snacks, which are often high in omega-6-rich vegetable oils.
- Choose healthier cooking oils like olive oil, avocado oil, or coconut oil instead of corn, soybean, or sunflower oil.
- Limit intake of processed meats and fast foods, which are often high in omega-6s.
- Opt for Grass-Fed Meat:
- Grass-fed beef and dairy products generally have a better omega-3 to omega-6 ratio compared to grain-fed alternatives.
- Incorporate Omega-3 Rich Eggs:
- Choose eggs from hens fed a diet rich in omega-3s, often labeled as “omega-3 enriched” eggs.
- Snack on Nuts and Seeds Wisely:
- While nuts and seeds are healthy, some are higher in omega-6s. Favor walnuts, which have a good omega-3 to omega-6 ratio.

The Role of Supplements
While it’s always best to get nutrients from whole foods, omega-3 supplements can be beneficial, especially for those who don’t consume enough fatty fish. However, it’s important to choose high-quality supplements and consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.The American Heart Association recommends:
- For general health: Eat fatty fish at least twice a week.
- For those with heart disease: Consume about 1 gram of EPA+DHA per day, preferably from fatty fish
Beyond Omega-3 and Omega-6: The Omega-9 Connection
While we’ve focused primarily on omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, it’s worth mentioning omega-9 fatty acids. Unlike omega-3s and omega-6s, omega-9s are not considered essential because our bodies can produce them. However, they still play important roles in our health.The most common omega-9 fatty acid is oleic acid, which is found in high concentrations in olive oil. Omega-9s have been associated with several health benefits, including:
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Reduced inflammation
- Better heart health when used to replace saturated fats in the diet
Including sources of omega-9s, such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts like almonds and macadamias, can contribute to a well-rounded, healthy fat profile in your diet.
The Future of Omega Fatty Acid Research
As our understanding of nutrition evolves, so does our knowledge of omega fatty acids. Recent research has shed light on new potential benefits and applications of these essential nutrients:
- Personalized Nutrition: Emerging research suggests that individual genetic variations may affect how we metabolize and benefit from different omega fatty acids. This could lead to more personalized dietary recommendations in the future.
- Mental Health Applications: While initial studies have shown promise for omega-3s in managing depression and other mental health conditions, more research is needed to fully understand their potential in this area
- Autoimmune Disease Management: Omega-3s show potential in managing symptoms of various autoimmune diseases, but more large-scale studies are required to establish definitive guidelines
- Cognitive Health in Aging: As the global population ages, there’s increasing interest in the role of omega-3s in maintaining cognitive function and potentially reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline
Conclusion
Balancing your omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acid intake is a crucial aspect of maintaining optimal health. By understanding the roles these essential nutrients play in our bodies and making informed dietary choices, we can harness their benefits and potentially reduce the risk of various chronic diseases.Remember, while omega-3s often steal the spotlight, the key lies in achieving the right balance. A diet rich in whole foods, including fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and healthy oils, can go a long way in helping you maintain this balance. As always, if you’re considering significant changes to your diet or thinking about supplements, it’s wise to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.By making conscious choices about the fats we consume, we can take a significant step towards better health, supporting our hearts, brains, and overall well-being. The omega balance is not just about numbers; it’s about nourishing our bodies with the right nutrients in the right proportions. So, let’s embrace the omega edit and make balanced, essential fatty acids a cornerstone of our dietary habits.
FAQs
Q1. How much omega-3 should I consume daily?
The American Heart Association recommends eating fatty fish at least twice a week. For those with heart disease, about 1 gram of EPA+DHA per day is recommended, preferably from fatty fish
Q2. Can I get enough omega-3s from plant sources alone?
While plant sources provide ALA, which can be converted to EPA and DHA, the conversion rate is generally low. For optimal intake, including marine sources of omega-3s or considering a supplement may be beneficial.
Q3. Are there any risks associated with consuming too much omega-3?
While omega-3s are generally safe, very high doses may increase bleeding risk in some people. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting high-dose supplements.
Q4. How can I tell if I have the right balance of omega-3 and omega-6 in my diet?
While there’s no simple at-home test, focusing on whole foods, reducing processed food intake, and including regular servings of fatty fish can help improve your omega balance.
Q5. Can omega-3 supplements replace eating fish?
While supplements can be beneficial, they don’t provide the full range of nutrients found in whole fish. Whenever possible, it’s best to get omega-3s from dietary sources.
